Linux磁盘分区与格式化
linux磁盘表示方法介绍
硬盘命名方式
| OS | IDE(并口) | SATA(串口) | SCSI |
|---|---|---|---|
| CentOS6 | /dev/hda | /dev/sda | /dev/sda |
| CentOS7 | /dev/sda | /dev/sda | /dev/sda |
| CentOS8 | /dev/sda | /dev/sda | /dev/sda |
磁盘设备的命名
/dev/sda2
s=硬件接口类型(sata/scsi),d=disk(硬盘),a=第1块硬盘(b,第二块),2=第几个分区
/dev/hd h=IDE硬盘 /dev/hdd3
/dev/vd v=虚拟硬盘 /dev/vdf7
HP服务器硬盘
/dev/cciss/c0d0 /dev/cciss/c0d0p1 c0第一个控制器, d0第一块磁盘, p1分区1 /dev/cciss/c0d0p2 c0第一个控制器, d0第一块磁盘, p2分区2
磁盘分区、格式化
新增一块磁盘时:
- 对磁盘进行分区,以建立可用的 partition ;
- 对该 partition 进行格式化 (format),以建立系统可用的 filesystem;
- 若想要仔细一点,则可对刚刚建立好的 filesystem 进行检验;
- 在 Linux 系统上,需要建立挂载点 (亦即是目录),并将他挂载上来;
磁盘和分区信息查看
lsblk 列出系统上的所有磁盘列表




blkid 列出块设备的 UUID 等参数


parted 列出磁盘的分区表类型与分区信息

新增与删除分区
gdisk(GPT分区)
随便玩 gdisk ,只要离开 gdisk 时按下『q』,那么所有的动作『都不会生效!』相反的, 按下『w』就是动作生
效的意思。
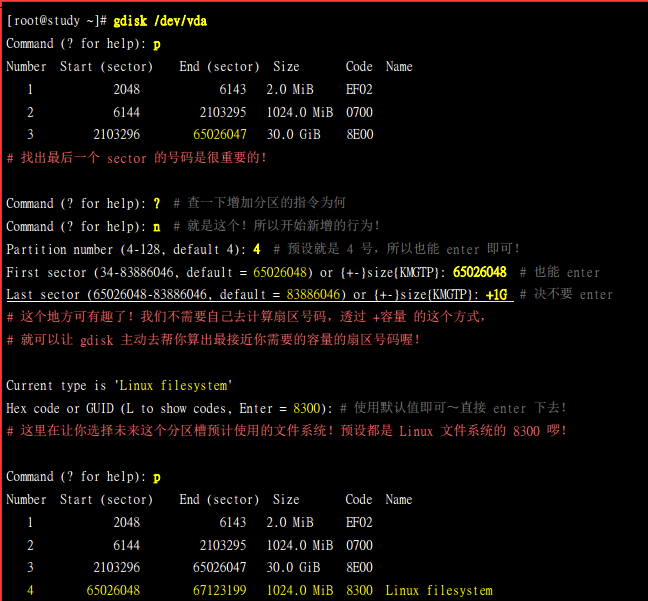
文件系统类型:
Command (? for help): L
0700 Microsoft basic data 0c01 Microsoft reserved 2700 Windows RE
4200 Windows LDM data 4201 Windows LDM metadata 7501 IBM GPFS
7f00 ChromeOS kernel 7f01 ChromeOS root 7f02 ChromeOS reserved
8200 Linux swap 8300 Linux filesystem 8301 Linux reserved
8e00 Linux LVM a500 FreeBSD disklabel a501 FreeBSD boot
a502 FreeBSD swap a503 FreeBSD UFS a504 FreeBSD ZFS
a505 FreeBSD Vinum/RAID a580 Midnight BSD data a581 Midnight BSD boot
a582 Midnight BSD swap a583 Midnight BSD UFS a584 Midnight BSD ZFS
a585 Midnight BSD Vinum a800 Apple UFS a901 NetBSD swap
a902 NetBSD FFS a903 NetBSD LFS a904 NetBSD concatenated
a905 NetBSD encrypted a906 NetBSD RAID ab00 Apple boot
af00 Apple HFS/HFS+ af01 Apple RAID af02 Apple RAID offline
af03 Apple label af04 AppleTV recovery af05 Apple Core Storage
be00 Solaris boot bf00 Solaris root bf01 Solaris /usr & Mac Z
bf02 Solaris swap bf03 Solaris backup bf04 Solaris /var
bf05 Solaris /home bf06 Solaris alternate se bf07 Solaris Reserved 1
bf08 Solaris Reserved 2 bf09 Solaris Reserved 3 bf0a Solaris Reserved 4
bf0b Solaris Reserved 5 c001 HP-UX data c002 HP-UX service
ed00 Sony system partitio ef00 EFI System ef01 MBR partition scheme
ef02 BIOS boot partition fb00 VMWare VMFS fb01 VMWare reserved
fc00 VMWare kcore crash p fd00 Linux RAID
新建分区步骤
新建gpt分区:
gdisk命令

记得按w保存(q是不保存离开),接着会警告可能出现的问题

partprobe 更新 Linux 核心的分区表信息
partprobe -s

删除分区也要更新分区表信息!!
删除分区
将刚刚建立的 /dev/vda6 删除
root@study ~]# gdisk /dev/vda
Command (? for help): p
Number Start (sector) End (sector) Size Code Name
1 2048 6143 2.0 MiB EF02
2 6144 2103295 1024.0 MiB 0700
3 2103296 65026047 30.0 GiB 8E00
4 65026048 67123199 1024.0 MiB 8300 Linux filesystem
5 67123200 69220351 1024.0 MiB 0700 Microsoft basic data
6 69220352 70244351 500.0 MiB 8200 Linux swap
Command (? for help): d
Partition number (1-6): 6
Command (? for help): p
# 你会发现 /dev/vda6 不见了!非常棒!没问题就写入吧!
Command (? for help): w
# 同样会有一堆讯息!鸟哥就不重复输出了!自己选择 y 来处理吧!
[root@study ~]# lsblk
# 你会发现!怪了!怎么还是有 /dev/vda6 呢?没办法!还没有更新核心的分区表啊!所以当然有错!
[root@study ~]# partprobe -s
[root@study ~]# lsblk
# 这个时候,那个 /dev/vda6 才真的消失不见了!了解吧!
fdisk (MBR分区)
在linux 下大磁盘的分区不能再采用fdisk了,MBR分区表只支持2T磁盘,所以大于2T的磁盘必须使用GPT分区表。
MBR适用于小磁盘空间,已经渐渐被淘汰了。
fdisk 跟 gdisk 使用的方式几乎一样!只是一个使用 ? 作为指令提示数据,一个使用 m 作为 提示这样而已。 此外,fdisk 有时会使用磁柱 (cylinder) 作为分区的最小单位,与 gdisk 默认使用 sector 不太一样。
另外,MBR 分区是有限制的 (Primary, Extended, Logical...)!
mkfs - 磁盘分区格式化
分区完后自然是进行格式化了。
XFS 文件系统 mkfs.xfs
格式化为xfs格式的文件系统。
使用命令:mkfs.xfs
mkfs.xfs 有很多参数,一般直接使用默认参数即可,速度更快
[root@study ~]# mkfs.xfs /dev/vda4
meta-data=/dev/vda4 isize=256 agcount=4, agsize=65536 blks
= sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1
= crc=0 finobt=0
data = bsize=4096 blocks=262144, imaxpct=25
= sunit=0 swidth=0 blks
naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0 ftype=0
log =internal log bsize=4096 blocks=2560, version=2
= sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1
realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0
# 很快格是化完毕!都用默认值!较重要的是 inode 与 block 的数值
[root@study ~]# blkid /dev/vda4
/dev/vda4: UUID="39293f4f-627b-4dfd-a015-08340537709c" TYPE="xfs"
# 确定建置好 xfs 文件系统了!
EXT4 文件系统 mkfs.ext4
mkfs.ext4 [-b size] [-L label] 装置名称
选项与参数:
-b :设定 block 的大小,有 1K, 2K, 4K 的容量,
-L :后面接这个装置的标头名称。
范例:将 /dev/vda5 格式化为 ext4 文件系统
[root@study ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/vda5
mke2fs 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013)
Filesystem label= # 显示 Label name
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2) # 每一个 block 的大小
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks # 跟 RAID 相关性较高
65536 inodes, 262144 blocks # 总计 inode/block 的数量
13107 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=268435456
8 block groups # 共有 8 个 block groups 喔!
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8192 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (8192 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
dumpe2fs
显示ext2、ext3、ext4文件系统的超级快和块组信息。此命令的适用范围:RedHat、RHEL、Ubuntu、CentOS、SUSE、openSUSE、Fedora。
[root@study ~]# dumpe2fs -h /dev/vda5
dumpe2fs 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013)
Filesystem volume name: <none>
Last mounted on: <not available>
Filesystem UUID: 3fd5cc6f-a47d-46c0-98c0-d43b072e0e12
....(中间省略)....
Inode count: 65536
Block count: 262144
Block size: 4096
Blocks per group: 32768
Inode size: 256
Journal size: 32M
其他文件系统
综合指令 mkfs
mkfs 按两次tab键,显示系统支持哪种文件系统的格式化功能
mkfs -t ext4 等同 mkfs.ext4
$ mkfs -h
Usage:
mkfs [options] [-t <type>] [fs-options] <device> [<size>]
Options:
-t, --type=<type> filesystem type; when unspecified, ext2 is used
fs-options parameters for the real filesystem builder
<device> path to the device to be used
<size> number of blocks to be used on the device
-V, --verbose explain what is being done;
specifying -V more than once will cause a dry-run
-V, --version display version information and exit;
-V as --version must be the only option